
Osteoarthritis of the knee joint, also called gonarthrosis, can significantly affect a person's quality of life. During the development of the disease, there is a gradual loss of hyaline cartilage in the joint. Little by little, the cartilage loses density and height. Its razvlecheniye and weight loss is noted, and over time it completely disappears. Consequently, there is no soft protective pad on the bone, and this leads to increased loading on the endplate of the innervated articular surface of the bone. As a result of this load, painful sensations develop. The code for osteoarthritis of the knee joint according to ICD-10 is M17.
The knee joint is affected quite often, as it is the knee that has a significant load during walking, physical exertion and running. In this case, uncomfortable movements can lead to soft tissue injury in the knee and lead to osteoarthritis. That is why gonarthrosis is one of the main causes of disability. According to statistics, this disease affects approximately 20% of the world's people to varying degrees.
Why osteoarthritis develops, how to prevent the development of this disease, which doctor treats osteoarthritis of the knee joint, and what kind of treatment methods can the doctor recommend after the diagnosis is made, will be discussed in thisArticle.
Pathogenesis
The disease develops in the context of a mismatch between the load on the joint and its ability to bear it. In this case, the properties of the cartilage can be determined by genetics or change due to the influence of acquired factors, both exogenous and endogenous. The development and progression of gonarthrosis can occur with age, against the background of obesity, due to dysplasia of the femoral-patellar joint or changes in the axis of the lower limb, disorders of the biomechanics of the joint, damageto the menisci and ligaments.
The basis of the pathogenesis is the predominance of catabolic over anabolic processes, which is observed in cartilaginous and subchondral bones, menisci, and synovium. As a result, structural changes occur and the biological properties of cartilage are lost. In addition, the pathological process extends to the muscles and ligaments.
The basis of articular cartilage is the matrix of connective tissue and chondrocytes. The connective tissue matrix contains type II collagen and aggrecan molecules. The shock-absorbing properties of cartilage are provided precisely by the connective tissue matrix.
The inflammatory process in osteoarthritis is not as intense as in arthritis. However, pro-inflammatory mediators are also present in osteoarthritis.
Classification
According to the origin of knee osteoarthritis, the following types are distinguished:
- Primary (idiopathic): develops without the influence of external causes.
- Secondary: certain factors lead to the development of the disease. Most often they are associated with injuries, fractures, surgical interventions on the joint, and inflammatory factors - acute and chronic arthritis.
The following degrees of knee osteoarthritis are also determined:
- Osteoarthritis of the first degree: it is determined in the period from the appearance of the first signs of the disease until the development of bone deformities visible on x-rays or during the examination. During this period, pain of varying intensity appears during movement.
- In grade 2- unpleasant sensations are observed even with the slightest effort. When walking and squatting, the knee contracts, the mobility of the joint decreases. The image shows the growth of bone tissue along the edges of the joint, as well as the narrowing of the joint space. On external examination, the knee can be seen to increase in size.
- In grade 3there is practically no cartilaginous tissue within the joint. If the disease progresses, the bones can grow together, resulting in total immobility of the leg. Sleep is disturbed, it becomes impossible to move without a cane or crutch.
The following types of this disease are also distinguished:
- Patellofemoral osteoarthritis of the knee- A condition in which degenerative changes are seen at the back of the patella, that is, the patella. With this form of the disease, the pain is mainly altered when descending a ladder or a mountain. Patellofemoral osteoarthritis can develop in runners. The disease is often diagnosed in young people.
- Post-traumatic osteoarthritis of the knee joint: consequence of the injury. The post-traumatic type of illness may not appear initially. But later, a person loses the complete motor activity of the joint.
Causes of osteoarthritis of the knee joint
Currently, work is being done to study the reasons that lead to the development of this pathology.
At the moment, the causes of knee osteoarthritis are associated with the influence of the following factors:
- Age: At a certain age, degenerative changes in tissues begin in a person and the ability of cartilage tissue to regenerate decreases.
- Arthritis: Over time, arthritis can lead to the development of osteoarthritis.
- Past injuries and overloads: In addition to injuries received, the development of the disease can lead to the need to kneel, squat, and lift weights frequently.
- Obesity and overweight: Due to excessive body weight, there is an increased load on the joints of the legs. In addition, substances that cause damage to the joint enter the bloodstream from the pathological adipose tissue and then into the joint.
- Heredity: In some cases, the development of the disease is determined by a defective gene responsible for the growth of cartilage tissue. As a consequence, this fabric may have a low resistance to damage. If close relatives have had osteoarthritis, this increases its probability.
- Diseases that lead to metabolic disorders - the risk of this pathology increases with atherosclerosis, diabetes mellitus.
- Hormonal disorders: more often, women get sick after 55 years.
- Sports: People who play certain sports are more likely to develop this disease. This is typical for runners, as well as soccer, tennis and basketball players.
Symptoms of knee osteoarthritis
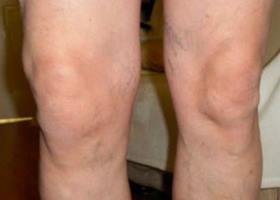
As a general rule, the symptoms of osteoarthritis of the knee joint increase slowly, as the process of its development takes years. If multiple joints are affected, symptoms of polyarthrosis develop.
The manifestations of the disease depend on its severity, age and other factors.
However, the main symptoms of knee osteoarthritis are the following:
- Pain in the knee joint, aggravated by activity. During rest, the knee hurts less.
- Swelling in the knee area.
- Sensation of heat in the joint.
- Unpleasant sensations of stiffness in the joint that appear after a person has been in a static position for a long time.
- Decreased range of motion of the knee joint, making it difficult for a person to get up from a chair, go down stairs, or get out of a car.
- Cracking and cracking in the knee, most commonly seen with sudden joint movements.
- Changes in the weather are believed to affect the degree of pain and discomfort.
Analysis and diagnosis
To determine if the disease can be cured, the diagnosis must be confirmed initially. In the process of diagnosis, the doctor examines and interviews the patient. But the most informative study in this case is a knee X-ray.
In addition, to clarify the diagnosis, it is advisable to undergo ultrasound, during which you can exclude arthritis, and also measure the height of the articular cartilage.
If necessary, designate additional exams.
Treatment of knee osteoarthritis
In order for the treatment of this disease to be as effective as possible, it is initially necessary to confirm the diagnosis and select the correct complex therapy scheme. Treatment of arthrosis of the knee joint at home is possible if the patient carefully follows all the recommendations of a specialist, practicing both drugs and additional treatment methods. Only in this case can home therapy be effective.
Drug treatment and other treatment methods for this disease are used depending on the degree of damage. The simplest is the treatment of osteoarthritis of the knee joint of the first degree. In case of a disease of the first degree, a complex therapy scheme is used, which allows you to get an effect in the shortest possible time. Therefore, if a person is diagnosed with first-degree osteoarthritis, the disease must be treated immediately.
As for how to treat osteoarthritis of the second degree knee joint, the doctor makes a decision based on the patient's condition. Since changes in cartilage tissue begin at this stage, treatment should be done immediately.
The possibility of curing grade 3 knee osteoarthritis depends on many factors. In grade 3, the cartilage becomes thinner, so treatment at this stage is longer and less effective.
Medications
The medical treatment of knee osteoarthritis is aimed at providing an analgesic and anti-inflammatory effect. It is also important to reduce the severity of cartilage destruction.
The following drugs are used for this purpose:
- Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs - tablets and local remedies are used - ointments, gels. The most efficient local and systemic application of these funds.
- Chondroprotectors for osteoarthritis of the knee joint: chondroprotectors from the group of glycosaminoglycans (hyaluronic acid), chondroitin sulfates and others are used. Such drugs for arthrosis of the knee joint are prescribed as part of a comprehensive treatment. The price of chondroprotectors depends on the drug and varies significantly.
- For serious illnesses, medications include steroids. Injections for osteoarthritis of the knee joint can be administered intramuscularly, as well as external agents with steroids can be used.
- External agents with skin irritants. In the description of folk remedies, you can also find annoying compresses.
- During treatment, the doctor may prescribe injections in the knee. Different drugs for injections in the knee joint can be used for osteoarthritis. In particular, corticosteroids are injected to relieve severe inflammation. Reviews of injections indicate that it is in this way that steroids work most quickly and effectively. The knee block can be performed not only with glucocorticosteroids, but also with anesthetics. Reviews of the blockade indicate that this method effectively relieves even severe pain. In addition, an injection may be made in the knee during treatment with chondroprotectants. Improves metabolic processes, activates collagen production. But to get the effect, you need to do at least five injections. Additionally, hyaluronic acid is injected intra-articularly, which improves the quality of intra-articular fluid and provides effective protection of cartilage tissue. Vitamins can also be administered intra-articularly.
- Plasmolifting method: its essence consists of the introduction of blood plasma rich in platelets in the affected knee.
- Medical bile for osteoarthritis of the knee joint - used for compresses. It should be noted that medical bile can be an effective remedy only if a doctor prescribes its use according to a certain scheme. Therefore, the option "we treat at home" without consulting a doctor is unacceptable in this case.
Procedures and operations
For osteoarthritis and polyarthrosis, non-pharmacological treatment methods are also used, the use of which is no less effective.
Physiotherapy. Various techniques are used, including shock wave therapy method, myostimulation, phonophoresis, ozone therapy, kinesitherapy, and others. Physical therapy can reduce pain, relieve inflammation. Any physiotherapy prescribed by a doctor must be carried out exactly in the complex that the doctor advised.
Laser therapy: produces decongestant, analgesic and anti-inflammatory effects.
Ozone therapy: relieves pain, produces an anti-inflammatory effect that reduces the amount of hormonal agents used.
Knee braces for osteoarthritis of the knee joint: The use of these devices reduces the intensity of pain. In addition, the knee brace protects you from instability. But to get the desired effect, it is necessary to choose the right knee pads or a knee brace. There are many general tips on how to choose knee braces for knee osteoarthritis. In addition, many different models of such knee braces are offered, with movement restrictions, amplifiers and the like. But still, those who want to buy knee braces for osteoarthritis, it is advisable not to trust the opinions of users, but rather the doctor's recommendations. The price of an orthopedic knee brace depends on different characteristics: material, quality. Knee braces are especially relevant if the patient develops post-traumatic osteoarthritis. But patellofemoral osteoarthritis, as well as other types of the disease, can be treated with this method.
Therapeutic gymnastics for osteoarthritis of the kneeis an effective method that allows you to improve the condition and prevent surgery, provided that the person performs regular and persistent exercise therapy for osteoarthritisof the knee joint. Physical therapy exercises help to strengthen the muscles of the legs and stop the development of the pathological process. However, a set of exercises for osteoarthritis of the knee joint should be performed in a certain sequence, and such gymnastics is selected individually. Therefore, it is best that the basis of the classes is not a gymnastics video, but a set of exercises developed by a doctor. In this case, it is not only the load that is important, but a complete exercise therapy.
With a similar pathology, different types of exercise therapy can be practiced.
Special gymnastics.These exercises are recommended both during treatment and for people over 40 for prevention. Knee exercises should be done every day. Similar exercises are also suitable for older people, as they can be performed at a leisurely pace.
Massage and manual therapy: suitable for patients with limited mobility, can be combined with exercise therapy. In the absence of the opportunity to visit a masseur, self-massage can be performed according to the scheme that will be demonstrated by the specialist.
As additional methods to improve the patient's condition and active rehabilitation, yoga, acupuncture, joint traction, special exercises on simulators (stationary bike and others) can be practiced.
If conservative methods are ineffective, surgical treatment is performed.
The following techniques can be used:
- Puncture: Getting rid of excess fluid in the joint can reduce symptoms of inflammation and restore mobility.
- Arthroscopy: can be performed by endoscopy. With this technique, the joint surfaces are cleaned of fragments of destroyed cartilaginous tissue.
- Periarticular osteotomy: During such an operation, one of the bones that make up the knee joint is cut and fixed again at a different angle. As a result, the severity of the pain decreases and the mobility of the knee increases. The intervention is effective in the first and second degree of the disease.
- Endoprosthesis: replacement of the knee joint with a special biocompatible construction. It is a very complex intervention, which is performed with the third degree of the disease.
Treatment of osteoarthritis of the knee joint with home remedies
Numerous reviews of the treatment of folk remedies for this disease confirm that such methods can be used as adjuncts, alleviating the patient's condition. However, such methods should not replace the main treatment. Home remedies are used for rubbing, compresses, baths, ingestion. Any thematic forum contains a lot of advice on this topic.
- Rub with garlic. Several garlic cloves should be peeled and minced. Mix the resulting porridge with 200 ml of vegetable oil and insist in a dark place for a week. Apply to the knee overnight with a film and a warm cloth on top.
- Mustard grind. To prepare the remedy, take 50 g of camphor and mustard powder, 500 ml of vodka, the protein from one egg. They are all mixed and stored in a jar in a dark place for a week. Next, the product should be rubbed on the knee three times a day.
- Elecampane Grind. Pour 50 g of helenium root with 125 ml of vodka and insist for two weeks. Rub twice a day.
- Burdock compresses. Burdock is a popular folk remedy for treating osteoarthritis. Several leaves of burdock should be folded down with the downy side and greased with vegetable oil. Attach them to the knee and cover them with cellophane and a warm cloth on top. Also, burdock leaves can be greased with vodka. The compress is applied at night. Likewise, the treatment with horseradish leaves is carried out.
- Cabbage leaf. It is also applied to the painful area at night. Pre-it is spread with honey, cologne, or vodka.
- honey compress. It is necessary to mix equal parts of honey, ammonia (10%), glycerin and medical bile, add a few drops of iodine. Leave the premixed product in a dark place for 10 days. Warm up before applying the compress.
- Onion decoction. It is taken internally. To prepare the broth, you need to take two large onions, cut them and pour 1 liter of water. Cook until the onions are tender. Take a 100 ml decoction three times a day.
- Celery juice. Grind the celery stalks in a blender, squeeze the juice. Drink 100 ml of juice three times a day.
- Gelatin. For osteoarthritis, it is recommended to consume foods that contain gelatin. It is recommended to include in the menu gelatin, gelatin and other dishes with gelatin.
- Bath with pine needles. Pour boiling water over 1 kg of pine needles and let it steep for several hours. Add to a warm bath, in which you can also dissolve 0. 5 kg of salt. Take a bath for 20-30 minutes.
Prevention
To prevent the development of osteoarthritis of the knee joint, the following preventive measures should be observed:
- Eat well and introduce a variety of foods that contain vitamins and minerals to your diet.
- Avoid excessive loads on the knee joint, protect it from injury.
- Stop bad habits.
- Keep track of weight, prevent obesity.
- Treat all diseases in time, take preventive examinations.
- Play sports and prefer mild physical activity.
- Wear high-quality footwear that is as comfortable as possible.
- Make sure you have a correct posture.
Diet for osteoarthritis of the knee joints

- Efficacy: healing effect
- Conditions: permanently
Diet is very important during treatment and rehabilitation. First of all, the food must be healthy and light; It is important to prevent excessive weight gain, which can aggravate the condition and lead to acute osteoarthritis. But the acute course of the disease requires not only treatment, but also weight loss.
It is also important to include in the diet foods that contain important components for cartilage tissue:
- Birds, rabbit.
- Sea fish.
- Soy products.
- Eggs.
- Greens, zucchini, carrots, pumpkin.
- Walnuts.
- Fruits, berries.
- Vegetable oils.
- Dishes with gelatin.
At the same time, you must limit the consumption of such products:
- Beans, sorrel, spinach, tomatoes.
- Plates of flour.
- Animal fat.
- Spices, vinegar.
- Alcohol.
- Red meat
You should eat frequently, in small portions. You should also drink about 2 liters of fluid a day.
Consequences and complications
If treatment is not carried out immediately, osteoarthritis can lead to the following complications:
- Inflammatory process of the periarticular tissues.
- Limitation of joint mobility.
- Changing the shape of the joints.
- Degeneration of the hip joint.
Such complications can lead to the development of disability and irreversible changes.
Forecast
It is important to treat the disease in a timely manner. The most favorable prognosis will be if you start treatment in 1 or 2 stages of the disease.



































